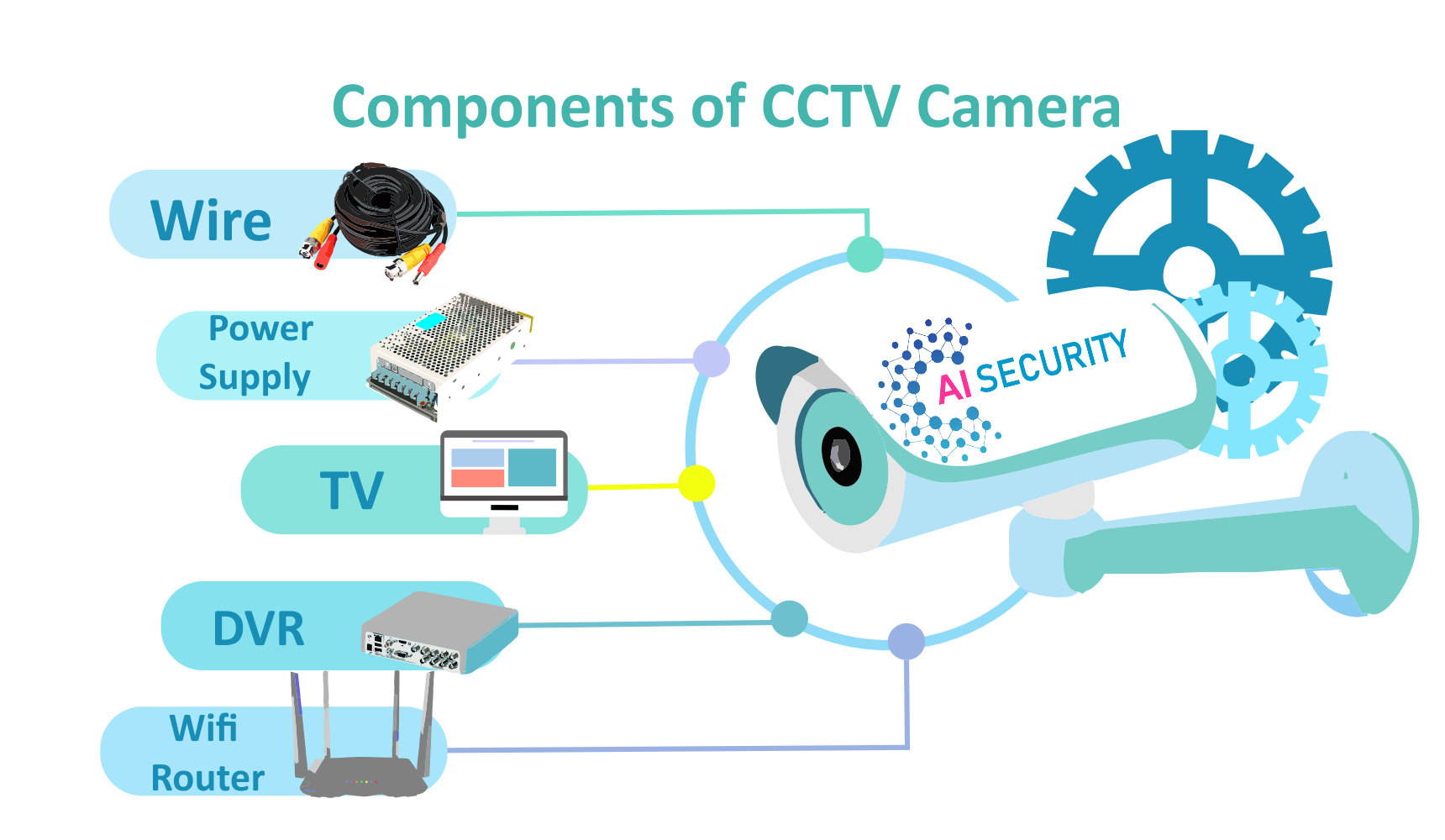
DVR
What is a Digital Video Recorder (DVR)?
A Digital Video Recorder (DVR) is a device that records video in a digital format to a disk drive, USB flash drive, SD memory card, SSD or other local or networked mass storage device. DVRs are typically used to record television programming, although they can also be used to record other video sources, such as security cameras.
DVRs allow users to pause, rewind, and fast-forward through recorded content, as well as schedule recordings of CCTV cameras. Some DVRs also have built-in personal video recorder (PVR) functions, which allow users to pause and resume live coverage.
DVRs are easy to set up and use. Some DVRs can be connected to the internet, allowing users to access their recorded content from anywhere with an internet connection.
DVR Hardware Features
There are a few key hardware features that are common to many DVRs. These features can vary depending on the specific model and manufacturer, but they generally include:
1. Disk drive:
Most DVRs include a hard disk drive (HDD) to store recorded video. The size of the HDD can vary, with larger drives allowing for more hours of recorded video.
2. Inputs and outputs:
DVRs typically have a variety of inputs and outputs to allow for the connection of various video sources and displays. These may include HDMI, component, composite, and S-video inputs and outputs, as well as Ethernet and USB ports.
3. Remote control:
Most DVRs come with a remote control to allow users to easily navigate and control the device from a distance.
4. On-screen display (OSD):
Many DVRs have an on-screen display that shows information about the device’s settings and current status. The OSD may also include a menu system for accessing various features and settings.
5. Processor and memory:
DVRs typically include a processor and memory to handle the tasks of recording, storing, and playing back video. The speed and capacity of these components can affect the performance of the DVR.
6. Power supply:
DVRs require a power supply to operate, which is usually included in the device. Some DVRs may also have an internal battery as a backup power source.
DVR Software Features
In addition to hardware features, many DVRs also include a range of software features that enhance their functionality. Some common software features found on DVRs include:
1. Scheduled recording:
Most DVRs allow users to schedule recordings of their CCTV cameras in advance. This can be done manually or through an electronic program guide (EPG).
2. Series recording:
Some DVRs have the ability to record an entire coverage, rather than just a single moment.
3. Time-shifting:
Many DVRs allow users to pause, rewind, and fast-forward through recorded content, as well as pause and resume coverage.
4. Picture-in-picture:
Some DVRs have the ability to display multiple video streams simultaneously, such as a live or recorded camera footage.
5. Streaming:
Some DVRs can be connected to the internet, allowing users to access their recorded content from anywhere with an internet connection.
6. Compatibility:
DVRs may be compatible with a variety of video formats, including standard definition (SD) and high definition (HD). They may also be compatible with different file formats, such as MP4, AVI, and MKV.
7. User interface:
Many DVRs have an easy-to-use interface that allows users to access and control the various features and settings of the device. This may include a menu system and on-screen display (OSD).


NVR
What is a Network Video Recorder (NVR)?
A Network Video Recorder (NVR) is a device that is used to record video footage from network cameras. It is typically used in video surveillance systems to store and manage video footage from security cameras.
NVRs are connected to a network and receive video streams from the cameras over the network. They have a built-in hard drive that is used to store the recorded video footage, and they can be accessed remotely over the network to view the recorded footage or to manage the system.
NVRs are different from Digital Video Recorders (DVRs), which are used to record video from analog cameras. DVRs are connected to the cameras directly using cables, while NVRs use a network connection.
NVRs are typically used in commercial and industrial settings, but they can also be used in residential settings for home security. They offer a number of benefits, including the ability to remotely access the recorded footage, the ability to scale the system by adding more cameras, and the ability to integrate with other systems such as alarm systems or access control systems.
Network Video Recorder (NVR) Features
There are a number of features that are commonly found in Network Video Recorders (NVRs). Here are a few examples:
1. Video recording and playback:
The primary function of an NVR is to record and store video footage from the connected cameras. NVRs typically have a built-in hard drive or support for external hard drives, and they can be configured to record continuously or on a schedule. NVRs also usually have a user interface that allows you to view and play back the recorded footage.
2. Remote access:
Many NVRs have the ability to be accessed remotely over the internet, either through a web browser or a mobile app. This allows you to view the live video feed from the cameras or to access the recorded footage from anywhere with an internet connection.
3. Motion detection:
NVRs have the ability to detect motion in the video feed from the cameras and can be configured to trigger recording or send notifications when motion is detected.
4. Alerts and notifications:
NVRs can be configured to send notifications or alerts to you when certain events occur, such as motion detection or loss of video feed from a camera.
5. Compatibility with a range of cameras:
NVRs are typically compatible with a range of network cameras, including both IP cameras and analog cameras that have been converted to digital using an encoder.
6. Integration with other systems:
Some NVRs have the ability to integrate with other systems such as alarm systems or access control systems, allowing you to manage multiple security systems from a single interface.
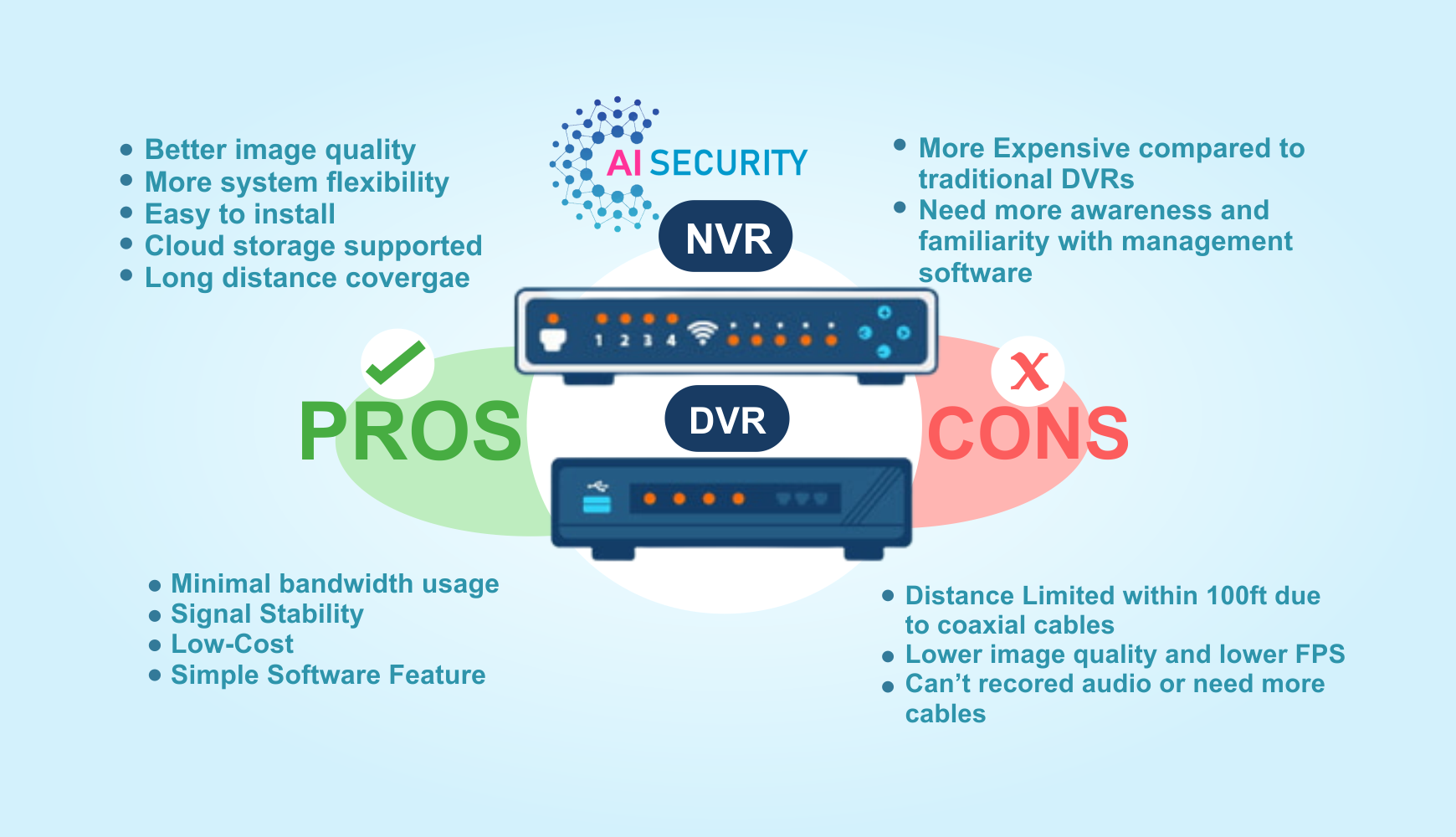
Network Video Recorders vs. Digital Video Recorders
Network Video Recorders (NVRs) and Digital Video Recorders (DVRs) are both used to record and store video footage for security and surveillance purposes. However, there are a few key differences between the two:
Connection type: NVRs are connected to the cameras over a network, while DVRs are connected directly to the cameras using cables.
Compatibility with cameras:
NVRs are typically compatible with both IP cameras and analog cameras that have been converted to digital using an encoder. DVRs, on the other hand, are only compatible with analog cameras.
Remote access:
NVRs can be accessed remotely over the internet, while DVRs typically cannot.
Scalability:
NVRs are generally more scalable than DVRs, as they can support a larger number of cameras and can be easily expanded by adding more cameras to the network.
Integration with other systems:
NVRs are often more flexible when it comes to integration with other systems, as they can be accessed over the network and can therefore be integrated with other systems that are also connected to the network.
Overall, NVRs are generally considered to be more advanced and flexible than DVRs, as they offer a number of benefits such as the ability to support a wide range of cameras, the ability to be accessed remotely, and the ability to integrate with other systems. However, DVRs can still be a good choice for smaller or simpler surveillance systems.